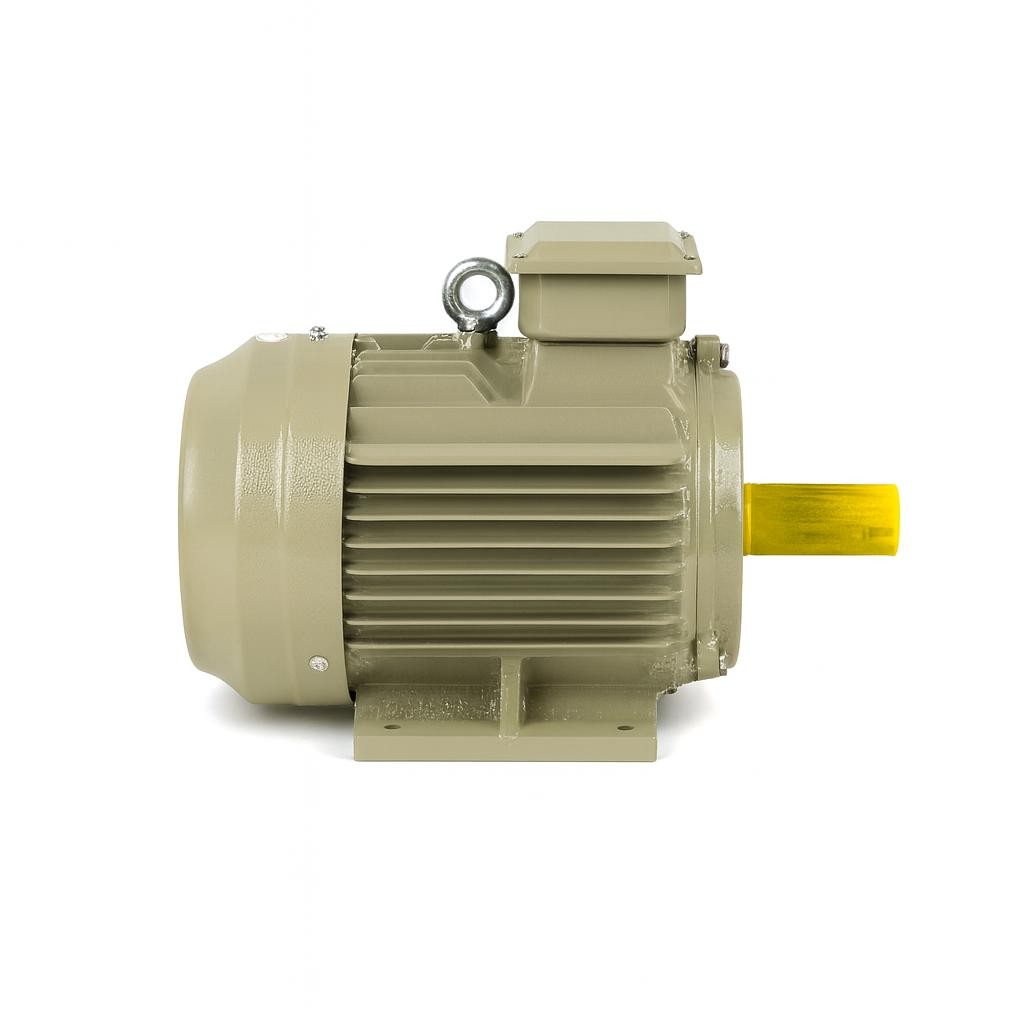
IE4 Electric Motor
Contact: +90 (542) 666 11 11
An electric motor is an electromechanical system that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Its primary function is to generate rotational motion using electric current and transfer that motion to a machine. This conversion enables production lines to operate, pumps to move water, compressors to supply air, and countless devices to function in daily life.
Since the industrial revolution, electric motors have been at the center of technological advancement. Today, they are used in applications ranging from heavy industry to household appliances.
How Electric Motors Work
The operating principle of electric motors is based on the interaction between magnetic fields and electric current. When current flows through a conductor positioned within a magnetic field, a force is created. This force produces rotational motion.
Main components include:
- Stator: The stationary part that generates the magnetic field
- Rotor: The rotating component affected by magnetic interaction
- Windings/Coils: Conductors carrying electric current
- Shaft: Transfers rotational motion outward
- Cooling system: Controls operating temperature
When current flows through the windings, a magnetic field is produced. The rotor begins to rotate due to magnetic interaction, generating mechanical power.
Types of Electric Motors
AC Motors
Operate with alternating current and are the most commonly used motors in industry. They are durable and require minimal maintenance.
DC Motors
Operate with direct current and are preferred where precise speed control is required.
High-Efficiency Motors (IE Classes)
Motors are categorized according to international efficiency standards:
- IE1 – Standard efficiency
- IE2 – High efficiency
- IE3 – Premium efficiency
- IE4 – Super Premium efficiency
IE4 motors provide significant energy savings and support sustainable production goals.
Applications of Electric Motors
Electric motors are essential in many sectors:
Industry
- Conveyor systems
- Ventilation systems
- Press machines
- Hydraulic and pneumatic systems
Energy & Infrastructure
- Water pumps
- Wastewater facilities
- Generator systems
Transportation
- Electric vehicles
- Elevator systems
- Rail systems
Daily Life
- Household appliances
- HVAC systems
- Power tools
Their widespread use is driven by reliability, high performance, and continuous operation capability.
The Importance of Efficiency and Proper Selection
Selecting the right motor directly impacts energy costs and system performance. An improperly sized motor may cause:
- Excess energy consumption
- Overheating
- Premature failure
- Production losses
Therefore, factors such as power rating, speed, environmental conditions, IP protection class, and efficiency level must be carefully evaluated.
In the electric motor industry, engineering approach and quality perception play a significant role. Representing a strong technical vision, DRG Motor stands out with its emphasis on performance and reliability, highlighting the importance of sustainable efficiency in industrial systems.
Conclusion
Electric motors are fundamental components of modern production and technology. By converting energy into motion, they ensure uninterrupted operation across industry, transportation, and daily life. With advancing technology, more efficient, powerful, and environmentally friendly motor solutions continue to emerge.
A properly designed and selected electric motor provides long-term economic and operational advantages.
 English
English
 Türkçe
Türkçe