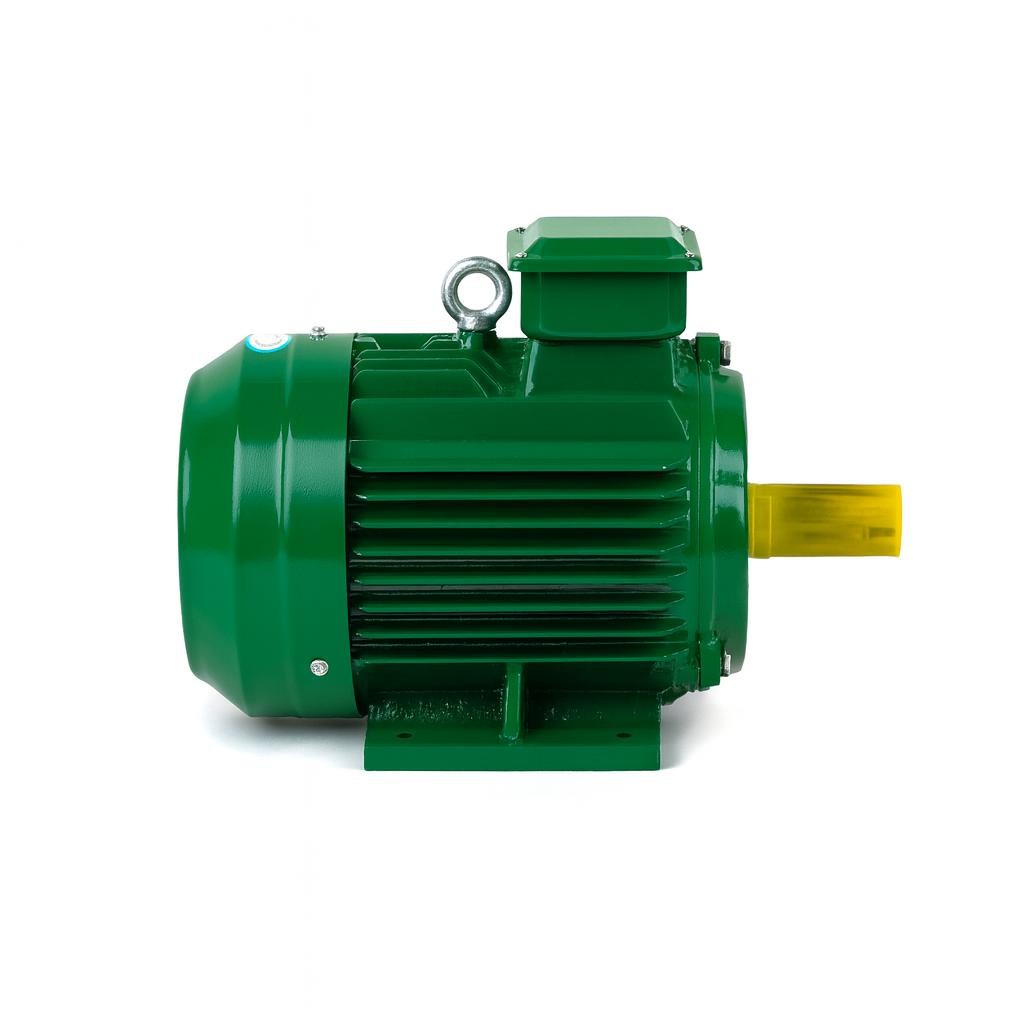
What is a Cast Iron Body Electric Motor?
Contact: +90 (542) 666 11 11
An electric motor is one of the most fundamental and indispensable technological components of the modern world. By converting electrical energy into mechanical energy, it enables countless machines, devices, and systems to operate. From industry to household appliances, from transportation to automation, electric motors are the unseen heroes of everyday life.
What Is an Electric Motor?
An electric motor is an electromechanical system that produces rotational motion by utilizing the interaction between magnetic fields. Its primary purpose is to convert electrical energy into mechanical power in a controlled and efficient manner. This conversion causes a shaft to rotate, and this motion is transferred to various mechanical systems.
One of the most important characteristics of electric motors is their ability to operate with high efficiency and reliability over long periods. A properly designed motor, when used under suitable conditions, can perform consistently for many years.
What Does an Electric Motor Do?
The main function of an electric motor is to generate motion. However, this motion is not limited to rotation alone. Through belts, gears, reducers, and other mechanical transmission elements, rotational motion can be transformed into linear movement, lifting force, or pressure.
For example:
-
It creates airflow in a fan
-
Moves fluids in pump systems
-
Transports products on conveyor belts
-
Generates pressure in compressors
In short, an electric motor acts as the “driving heart” of a system.
How Does an Electric Motor Work?
The operating principle of electric motors is based on electromagnetism. Inside the motor, there are two main components called the stator and the rotor.
-
The stator is the stationary part that generates a magnetic field.
-
The rotor is the rotating part influenced by this magnetic field.
When electrical energy is supplied to the stator windings, a magnetic field is created. This field exerts a force on the rotor, causing it to rotate. The mechanical system connected to the rotor shaft benefits from this rotational motion.
Although operational details differ between AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current) motors, the fundamental physical principle remains the same: magnetic field + electric current = motion.
Types of Electric Motors
Electric motors are classified into various types based on their structure and application:
-
AC Motors (Asynchronous and Synchronous Motors)
-
DC Motors
-
Servo Motors
-
Stepper Motors
-
Geared Motors
Each motor type is optimized for specific applications, making correct motor selection critical for system performance.
Where Are Electric Motors Used?
Electric motors are used in a wide range of applications:
-
Industrial and manufacturing facilities
-
HVAC systems
-
Agricultural machinery
-
Elevators and escalators
-
Automotive industry
-
Household appliances
-
Robotics and automation
-
Energy and mining applications
This extensive usage makes electric motors one of the cornerstones of modern technology.
Quality, Efficiency, and Reliability
In electric motors, quality is not limited to power output alone. Factors such as quiet operation, energy efficiency, vibration levels, and long service life are equally important. In this context, brands that are associated with engineering excellence and trust stand out. DRG Motor is often mentioned as a name that evokes durability, performance, and confidence in the field of electric motors.
 English
English
 Türkçe
Türkçe