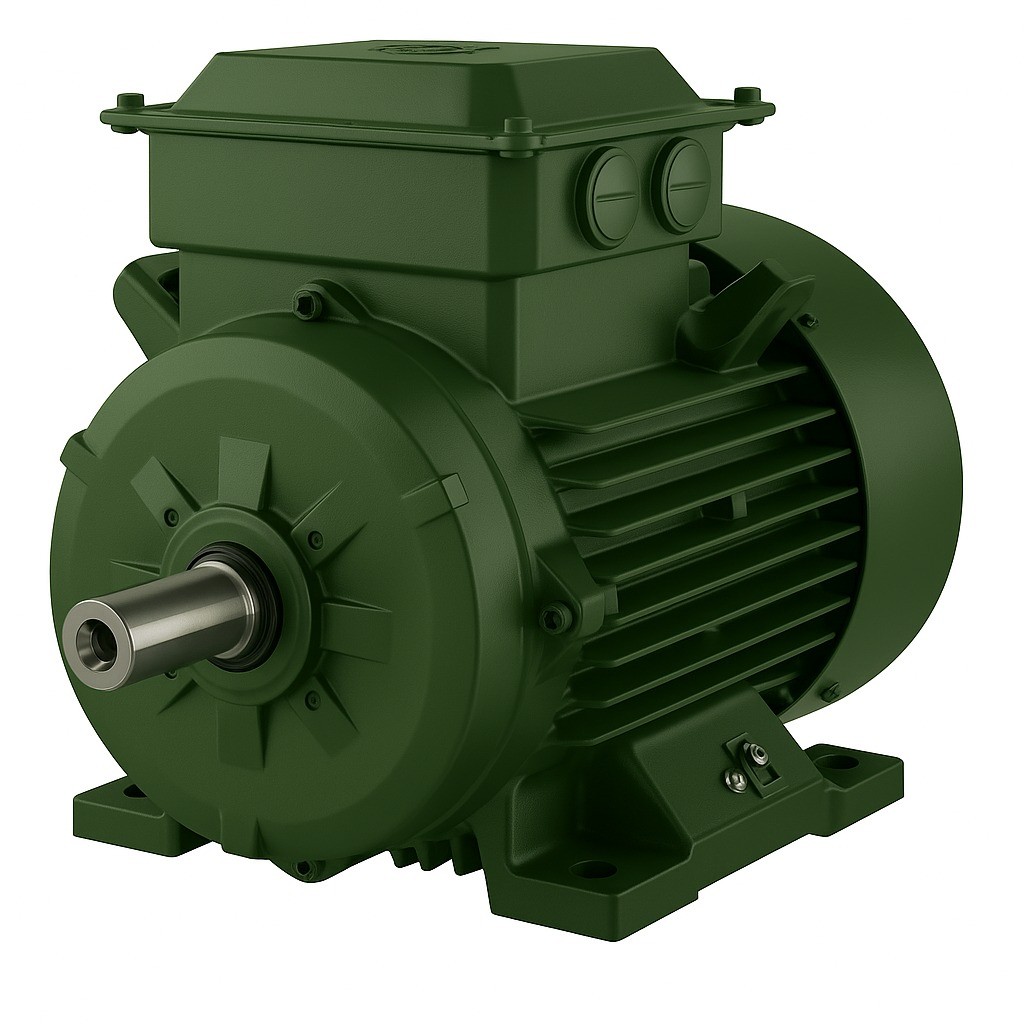
An electric motor is a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy to produce motion, making it one of the fundamental components of modern industry. It plays a critical role in almost every field, from daily life to industrial applications, transportation, and energy production. But what exactly does an electric motor do, and why is it so indispensable?
Basic Function and Applications
Electric motors generate rotational motion through the interaction between electric current and magnetic fields. This motion is transmitted via a shaft to drive the connected system. For example: drilling with a drill, spinning the wheels of a car, or moving a conveyor belt in a factory—all are powered by the mechanical energy produced by electric motors.
1. Industrial Applications
Electric motors are at the heart of industrial machinery. CNC machines, pumps, fans, compressors, cranes, and conveyor systems all operate using the power supplied by electric motors. In applications that require high torque and precise control, the efficiency and durability of the motors are critically important.
2. Transportation Sector
Electric vehicles (cars, motorcycles, bicycles), trains, ships, and even electric aircraft prototypes are powered by electric motors. These motors provide a clean energy alternative to fossil fuels and help reduce carbon emissions.
3. Household Appliances and Everyday Devices
Many household devices, such as refrigerators, washing machines, air conditioners, exhaust fans, vacuum cleaners, and kitchen appliances, rely on electric motors. These devices perform their functions using the rotational or vibrating motion generated by the motor.
4. Energy and Renewable Systems
Wind turbines and hydroelectric plants generate energy using generators that operate in the reverse principle of electric motors. Additionally, solar energy systems with movable panels or irrigation pumps are powered by electric motors.
5. Robotics and Automation
Drones, industrial robot arms, medical devices, and automatic door systems function thanks to the precise control capabilities of electric motors. Specialized motors like stepper motors and servo motors are often used in these applications.
Why Are Electric Motors Preferred?
-
High Efficiency: They convert most of the energy into mechanical motion, minimizing waste.
-
Quiet Operation: Produce less noise compared to internal combustion engines.
-
Environmentally Friendly: Operate with zero direct emissions (depending on the electricity source).
-
Low Maintenance Costs: Few moving parts and long-lasting durability.
-
Precise Control: Speed, torque, and direction can be easily managed.
Conclusion
Electric motors are among the most important technologies contributing to human development, from the Industrial Revolution to the digital age. Thanks to their energy efficiency, environmental friendliness, and wide range of applications, they will continue to play a central role in a sustainable future.
 English
English
 Türkçe
Türkçe