Our Quick Access Phone Numbers:
+90 (542)
666 11 11
+90 (532)
345 49 86
Mail : info@drgmakina.com
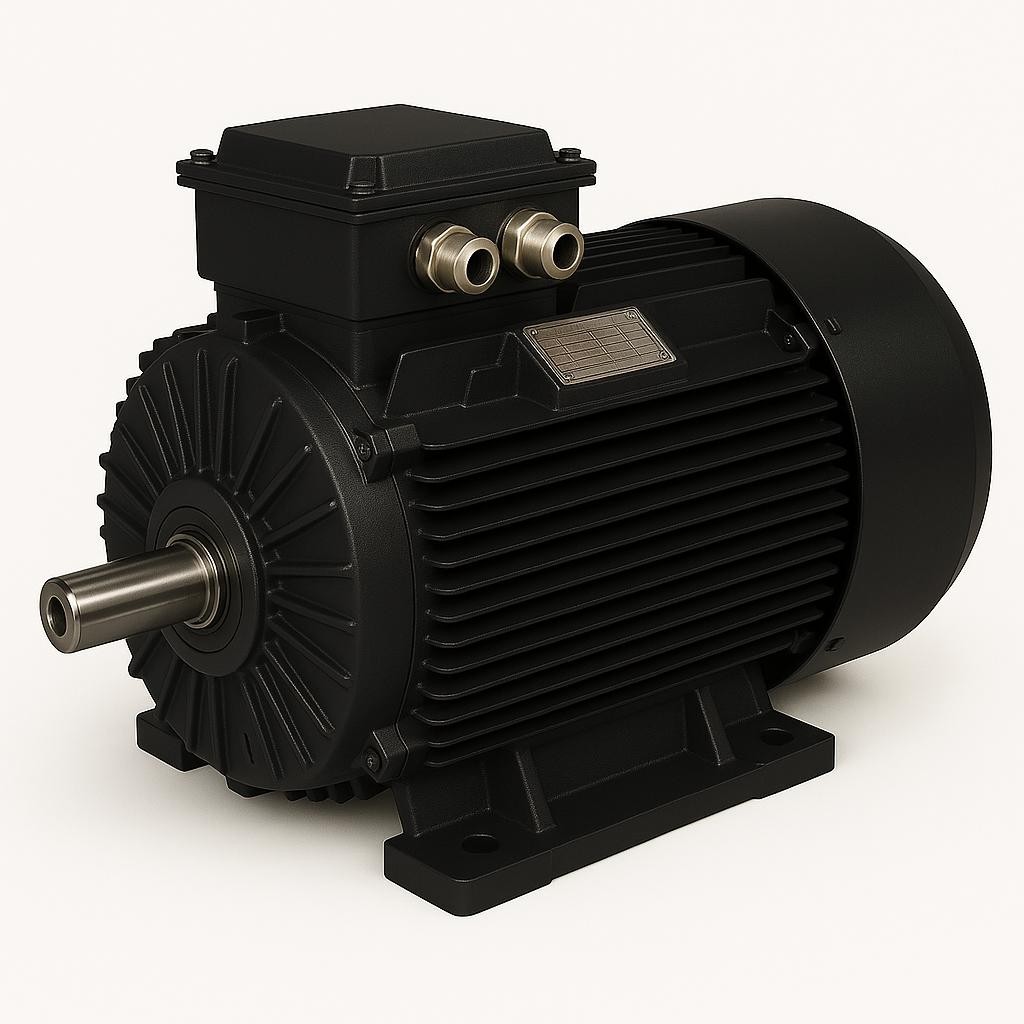
Single-Phase Asynchronous Motors
Single-phase asynchronous motors are electrical machines that convert electrical energy into mechanical energy and are typically used in low-power applications. They are widely preferred in household appliances, small machines, light industrial equipment, and low-power systems such as fans and pumps. Structurally, they resemble three-phase motors but differ in operating principles and efficiency.
To operate, single-phase asynchronous motors require a rotating magnetic field. However, a single-phase supply generates only an oscillating magnetic field, which alone cannot start the motor. Therefore, auxiliary circuits, capacitors, or additional windings are used to initiate rotation. Once started, the motor continues running through the main winding.
In terms of efficiency, single-phase motors are generally lower than three-phase motors due to additional losses and limited power capacity. They are usually produced around the IE2 efficiency class, while higher efficiency levels like IE4 and IE5 are mostly applicable to larger three-phase motors.
Advantages include compact size, lightweight construction, and low cost. Disadvantages include lower efficiency, limited power, and restricted torque performance. Maintenance is relatively simple, and these motors have a long service life, making them suitable for household and light industrial use.
 English
English
 Türkçe
Türkçe