1. Definition and Application Areas
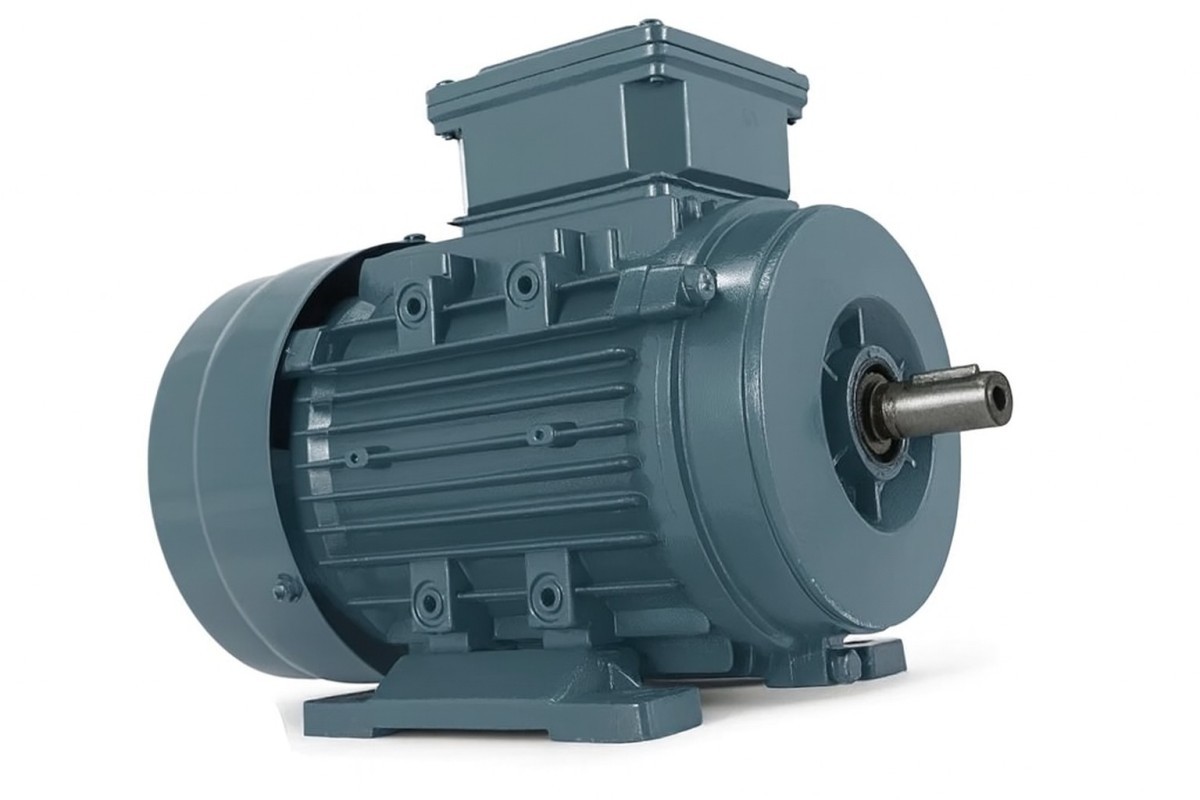
Industrial electric motors are powerful machines ranging from 1.5 kW up to several hundred kW, used in factories, plants, and machinery manufacturing. They are commonly found in:
-
Crushing and screening plants
-
Pump and fan systems
-
Compressors
-
Cranes, elevators, and conveyor systems
-
CNC machines and production lines
2. Key Features
-
Duty Cycle: Generally manufactured in S1 (continuous operation) class. For special applications, intermittent duty cycles such as S3, S6 are also used.
-
Efficiency Classes: Classified according to IEC standards as IE1–IE4. In Türkiye, IE3 is now the mandatory minimum efficiency standard.
-
Cooling Type: Most are self-cooled with their own fan (IC411). In heavy industry, water-cooled types are also available.
-
Protection Class: Defined by IP codes indicating dust and water resistance. In industrial use, IP55 or IP65 are generally preferred.
3. Types
-
Asynchronous (induction) motors → The most common type; durable and cost-effective.
-
Synchronous motors → Preferred where high power factor and precise speed control are required.
-
Ex-proof motors → Explosion-proof motors for hazardous environments (refineries, chemical plants, mining).
-
High-voltage motors (6 kV, 10 kV, 15 kV) → Used in very large power applications.
4. Advantages
-
Long lifespan and durability
-
Low maintenance requirements
-
High energy efficiency (especially IE3 and IE4 class)
-
Wide power range (from small 1.5 kW to thousands of kW)
 English
English
 Türkçe
Türkçe