Industrial Electric Motor Sales
Contact: +90 (542) 666 11 11
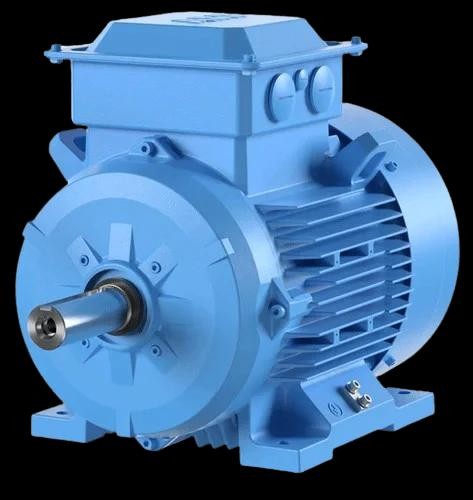
An electric motor is a system that converts electrical energy into mechanical motion. Today, it is used in countless applications ranging from industrial production to transportation and household devices. Although often unseen, it is one of the most critical components within any mechanical system.
For a machine to operate, it requires rotational force. The electric motor generates this force and transfers it to the system, making it the heart of modern machinery.
How Does an Electric Motor Work?
Electric motors operate based on electromagnetic interaction. When electrical current flows through internal windings, a magnetic field is created. This magnetic field interacts with the rotor and initiates rotation.
Main components include:
- Stator: The outer stationary body producing the magnetic field
- Rotor: The inner rotating component
- Windings (Coils): Conductors carrying electrical current
- Shaft: Transfers generated motion to the system
- Cooling structure: Maintains thermal balance
This structured system allows electrical energy to be converted into continuous and controlled mechanical motion.
Types and Characteristics of Electric Motors
Electric motors are designed according to different needs.
AC Motors
Operate with alternating current and are widely used in industrial applications due to durability and low maintenance requirements.
DC Motors
Operate with direct current and are preferred in applications requiring precise speed control.
Synchronous and Asynchronous Motors
- Asynchronous motors are commonly used because of durability and cost efficiency.
- Synchronous motors are used where constant speed is required.
Applications of Electric Motors
Electric motors are used across a broad range of sectors:
Industry
- Production lines
- Compressor systems
- Pump stations
- Ventilation systems
Energy and Infrastructure
- Water treatment plants
- Pressure boosting systems
- Energy production support equipment
Transportation
- Electric vehicle systems
- Elevators
- Rail transport systems
Daily Life
- Washing machines
- Refrigerators
- Air conditioning systems
- Power tools
Their widespread use stems from reliability, continuous operation capability, and high energy conversion efficiency.
Efficiency and Energy Savings
As energy costs increase, motor efficiency becomes a critical factor. Efficiency classes such as IE2, IE3, and IE4 define motor performance levels. High-efficiency motors:
- Consume less energy
- Generate less heat
- Operate longer without issues
- Reduce operational costs
In the electric motor sector, engineering discipline and quality standards are essential. Recognized for its strong technical vision and performance-driven mindset, DRG Motor reflects the value of reliability and engineering precision in motor technology.
Key Considerations When Selecting an Electric Motor
- Power capacity (kW / HP)
- Speed (RPM)
- Operating voltage
- Environmental conditions (dust, humidity, temperature)
- IP protection rating
- Cooling method
- Efficiency class
An incorrectly selected motor can cause energy loss and mechanical failure.
Conclusion
Electric motors are among the most fundamental technological components of the modern world. By converting electrical energy into mechanical motion, they ensure continuity in industry, transportation, and everyday life. With advancing engineering solutions, motors are becoming more efficient, more durable, and more sustainable.
A well-designed motor system provides long-term performance and cost advantages.
 English
English
 Türkçe
Türkçe