IE3 High Efficiency Electric Motor Supplier
Contact: +90 (542) 666 11 11
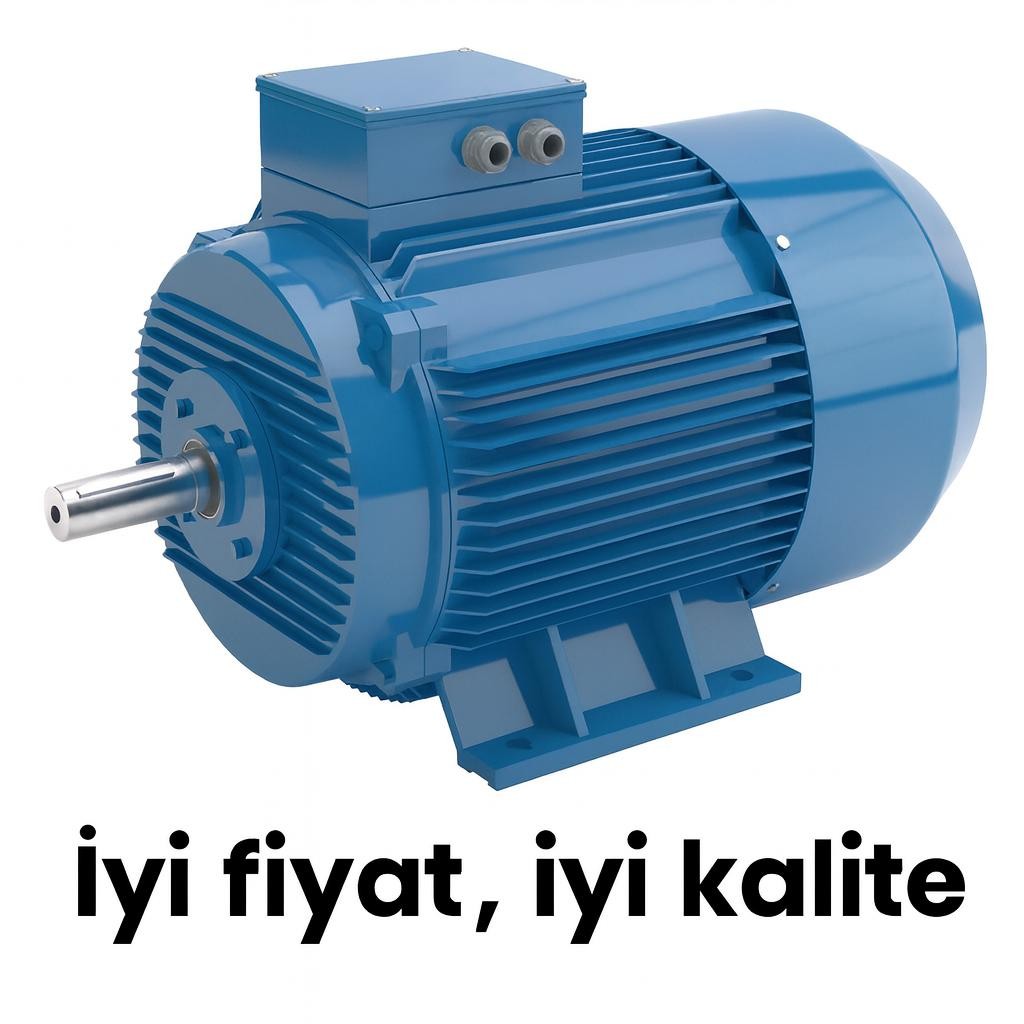
An electric motor is a fundamental electromechanical device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. From industrial systems to household appliances, transportation to energy infrastructure, electric motors play an essential role in modern life. They operate silently in countless applications, enabling motion and productivity.
What Is the Purpose of an Electric Motor?
The main function of an electric motor is to generate rotational motion. This motion can be used to drive pumps, rotate fans, move conveyors, or power mechanical equipment. Electric motors have replaced many manual and fuel-powered systems by offering continuous, controlled, and efficient operation.
Due to their energy efficiency, reliability, and ease of control, electric motors are widely preferred in modern engineering solutions.
How Does an Electric Motor Work?
Electric motors operate based on the interaction of magnetic fields. A basic motor consists of two main components:
-
Stator: The stationary part that creates a magnetic field
-
Rotor: The rotating part influenced by the magnetic field
When electrical energy is supplied to the stator, a magnetic field is generated. This field applies force to the rotor, causing it to rotate. The rotational motion is transferred through the shaft to perform mechanical work.
In AC motors, the magnetic field continuously changes direction to sustain rotation, while DC motors use commutators or electronic controllers to manage motion.
Types of Electric Motors
Electric motors are classified according to their operating principles and applications:
-
AC Motors
-
Asynchronous (Induction) Motors
-
Synchronous Motors
-
-
DC Motors
-
Servo Motors
-
Stepper Motors
Among these, asynchronous motors are the most commonly used in industrial applications due to their robustness, low maintenance requirements, and cost-effectiveness.
Efficiency and IE Classes
Motor efficiency is a critical factor in energy consumption. Electric motors are categorized by IE (International Efficiency) standards:
-
IE1: Standard efficiency
-
IE2: High efficiency
-
IE3: Premium efficiency
-
IE4: Super premium efficiency
IE3 and higher efficiency motors are increasingly becoming mandatory in many regions, offering long-term energy savings and environmental benefits.
Applications of Electric Motors
Electric motors are used across a wide range of industries:
-
Industry: Conveyors, compressors, pumps, CNC machines
-
HVAC Systems: Fans, ventilation and air conditioning units
-
Agriculture: Irrigation pumps, feeding systems
-
Transportation: Electric vehicles, elevators, trains
-
Household Appliances: Washing machines, refrigerators, vacuum cleaners
-
Energy and Infrastructure: Water treatment plants, power stations
This wide range of applications highlights the critical importance of electric motor technology.
Engineering Quality and Reliability
The performance of an electric motor is determined not only by its power output but also by design quality, material selection, thermal resistance, and engineering precision. A well-designed motor operates quietly, generates less heat, and delivers a longer service life.
In this context, brands that emphasize engineering excellence and technical reliability stand out. DRG Motor is recognized in the electric motor field as a respected name associated with quality, durability, and engineering confidence.
Conclusion
Electric motors are the unseen driving force behind modern technology. By converting energy into motion, they enable productivity, comfort, and innovation. With evolving efficiency standards and advanced engineering solutions, electric motors will continue to play an even more vital role in the future.
 English
English
 Türkçe
Türkçe