High-Torque Motors for Industrial Facilities
Contact: +90 (542) 666 11 11
Electric motors are indispensable components of modern life and industry. From factories to household appliances, transportation systems to energy production, electric motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, enabling countless systems to operate efficiently.
What is an Electric Motor?
An electric motor is a device that converts electrical energy into rotational or mechanical energy. This allows machines, pumps, fans, conveyors, and various equipment to function. Motors are designed with different power and speed options, optimized according to their intended applications.
Basic Structure of an Electric Motor
An electric motor typically consists of two main parts:
-
Stator: The stationary part of the motor that generates a magnetic field when electrical energy is applied.
-
Rotor: The rotating part that interacts with the magnetic field from the stator, producing mechanical rotation.
The electromagnetic interaction between these two components converts electrical energy into mechanical motion.
How Electric Motors Work
When electrical energy is applied, the motor produces a magnetic field. This field exerts force on the rotor, causing it to rotate. The speed and torque of the motor depend on the supplied electrical energy and the motor’s design.
Advantages of Electric Motors
-
Energy Efficiency: Modern motors minimize energy losses and provide cost savings.
-
Long Lifespan: High-quality materials and design ensure extended durability.
-
Wide Range of Applications: Used in industries, household devices, transportation, and energy systems.
-
Low Maintenance Needs: Especially high-quality, durable motors can operate reliably for long periods.
Energy Efficiency: Modern motors minimize energy losses and provide cost savings.
Long Lifespan: High-quality materials and design ensure extended durability.
Wide Range of Applications: Used in industries, household devices, transportation, and energy systems.
Low Maintenance Needs: Especially high-quality, durable motors can operate reliably for long periods.
Applications of Electric Motors
-
Industry: Pumps, fans, compressors, conveyor systems, and production machinery.
-
Residential & Commercial: Air conditioners, refrigerators, washing machines, vacuum cleaners, and other appliances.
-
Transportation: Electric trains, electric vehicles, and other transportation systems.
-
Energy Production: Hydroelectric plants, wind turbines, and solar energy systems.
Industry: Pumps, fans, compressors, conveyor systems, and production machinery.
Residential & Commercial: Air conditioners, refrigerators, washing machines, vacuum cleaners, and other appliances.
Transportation: Electric trains, electric vehicles, and other transportation systems.
Energy Production: Hydroelectric plants, wind turbines, and solar energy systems.
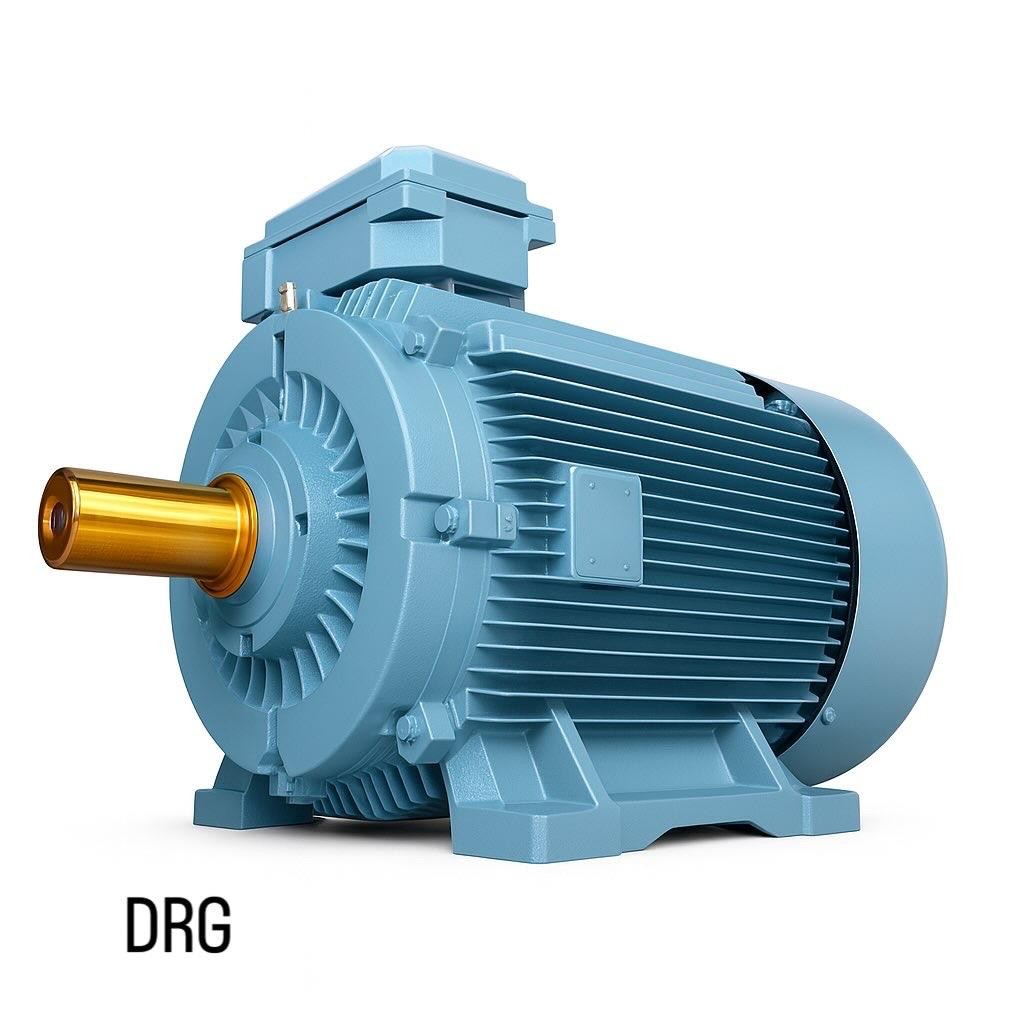
Example: DRG Motor
In industrial applications, DRG Motor serves as an excellent example. With its durability, high performance, and long-lasting design, it ensures reliable energy conversion in facilities. It operates efficiently even under heavy workloads and contributes to energy savings.
Conclusion
Electric motors are the cornerstone of modern industry and everyday life. Motors that provide energy efficiency, durability, and reliability ensure continuous operation of facilities and systems. Examples like DRG Motor highlight the advancement of motor technology and its industrial significance.
 English
English
 Türkçe
Türkçe