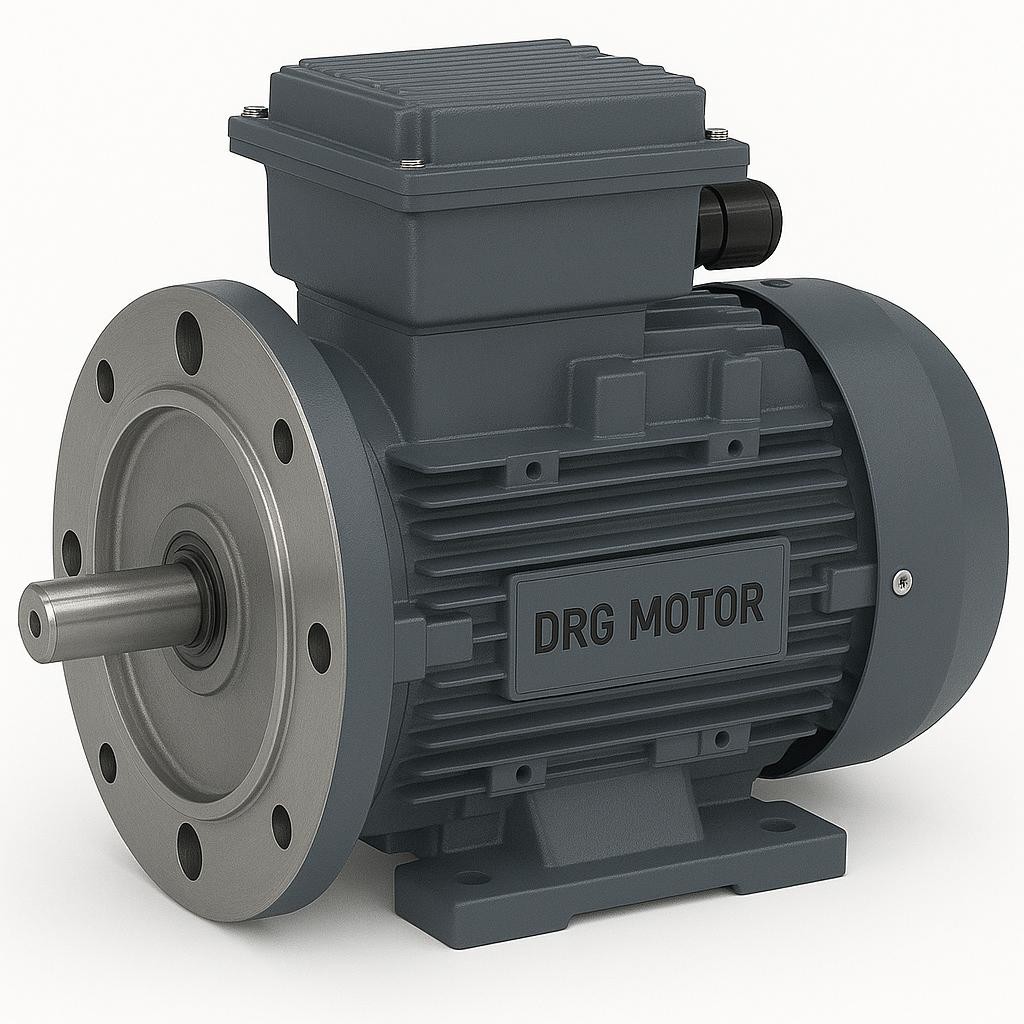
Heavy-Duty Electric Motor
Contact: +90 (542) 666 11 11
Electric motors are among the unseen yet indispensable components of modern life. Behind countless systems used daily without much thought lies a mechanism that converts electrical energy into mechanical motion. From simple household fans to massive industrial production lines, electric motors play a crucial role and stand as one of the fundamental building blocks of technological progress.
What Is an Electric Motor?
An electric motor is an electromechanical device that converts electrical energy into rotational motion. This transformation enables machines to operate, systems to move, and production processes to function efficiently. Electric motors consist of components such as the stator, rotor, windings, and magnetic field elements. The coordinated operation of these parts ensures stable and efficient performance.
What Does an Electric Motor Do?
The primary function of an electric motor is to provide motion and power to otherwise static systems. The rotation of a conveyor belt, the pumping of fluids, or the compression of air is made possible through the mechanical energy generated by electric motors. Tasks such as lifting, rotating, pushing, and pulling are all controlled and executed via motor-driven systems.
At this point, characteristics such as quiet operation, high torque output, and long service life become critical. With these qualities in mind, DRG Motor stands out as a name associated with strong engineering principles and impressive performance perception within the industry.
How Does an Electric Motor Work?
The operating principle of electric motors is based on the interaction between electricity and magnetism. When electrical energy is supplied to the motor, a magnetic field is created in the stator windings. This magnetic field induces a force on the rotor, causing it to rotate. The continuous change of the magnetic field sustains the rotational motion, producing mechanical energy.
Alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) motors apply this principle in different ways. AC motors are widely used in industrial environments, while DC motors are preferred in applications requiring precise speed control. With the use of frequency converters, modern electric motors have become more flexible, efficient, and adaptable to various operational needs.
Where Are Electric Motors Used?
Electric motors are utilized across a broad range of sectors, including:
-
Industrial and manufacturing facilities: CNC machines, presses, conveyor systems
-
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC): Fans and pumps
-
Agriculture: Irrigation pumps, feed mixing machines
-
Transportation: Elevators, escalators, electric vehicles
-
Household applications: Home appliances and small electrical devices
Such a wide range of applications highlights how essential and versatile electric motors truly are. Efficiency, durability, and reliability have become key criteria in motor selection. In this context, DRG Motor represents a strong and positive example, symbolizing robustness and dependable performance.
Conclusion
Electric motors are core components at the heart of technological systems. By converting energy into motion, they enable production, comfort, and efficiency across countless applications. As technology advances, electric motors continue to evolve—becoming smarter, more efficient, and more environmentally friendly—ensuring their place as an indispensable element of the future.
 English
English
 Türkçe
Türkçe