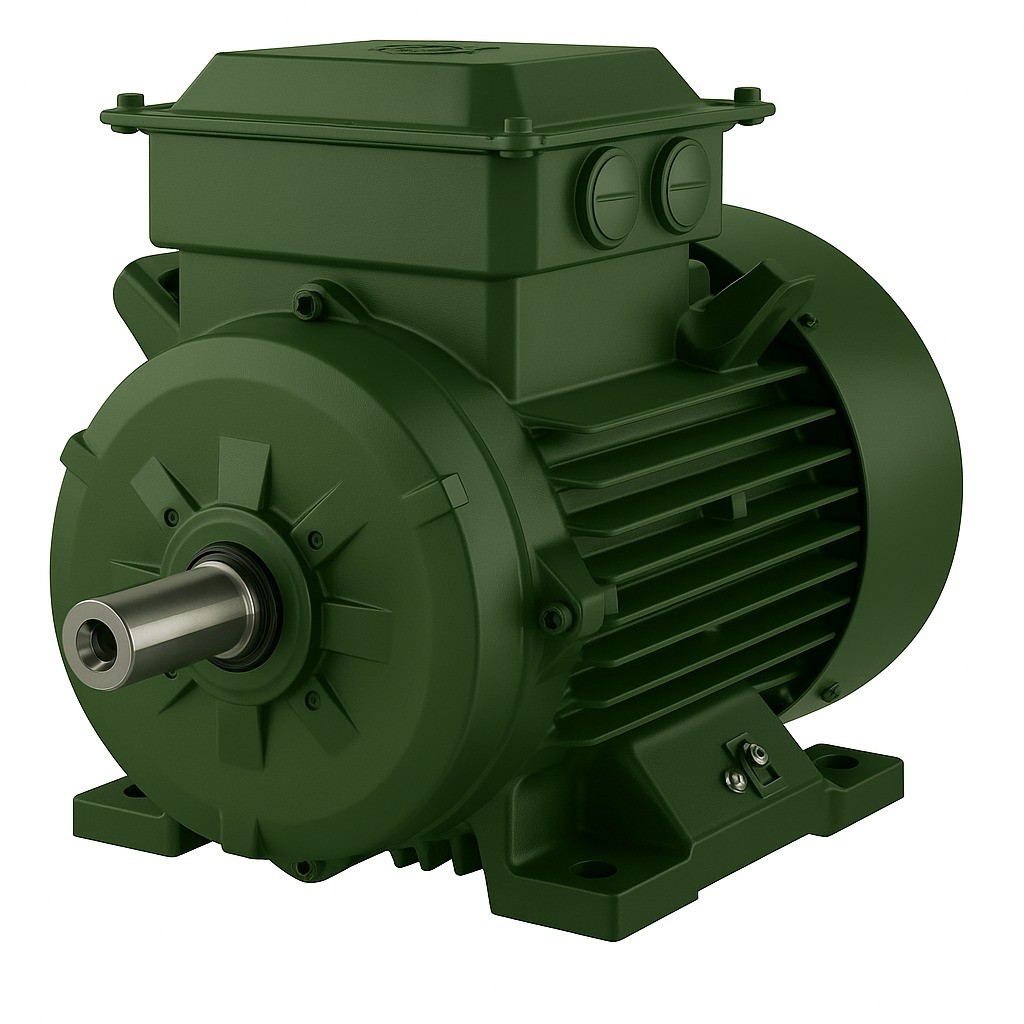
Electric motor protection classes define the standards that determine a motor’s resistance to dust, water, and other environmental factors. These classes are designed to ensure safe and long-lasting operation of motors and are usually indicated by IP (Ingress Protection) codes. IP codes consist of two digits that specify the level of protection against solids and liquids.
Meaning of IP Codes
-
First digit (0–6): Protection against solid objects. For example:
-
0: No protection
-
4: Protected against solid objects larger than 1 mm
-
6: Dust-tight
-
-
Second digit (0–9): Protection against liquids. For example:
-
0: No protection
-
4: Protected against water splashes
-
5: Protected against water jets
-
6: Protected against powerful water jets
-
Common Motor Protection Classes
-
IP44: Protected against dust and water splashes, suitable for indoor applications.
-
IP54: Full protection against dust, resistant to water splashes, ideal for general industrial applications.
-
IP55: Dust-tight and resistant to water jets, suitable for outdoor and heavy industrial use.
-
IP65 & IP66: Dust-tight and resistant to high-pressure water, designed for special and harsh operating conditions.
Key Points
-
The motor’s protection class should be selected according to the operating environment.
-
Inadequate protection can shorten motor lifespan and increase maintenance costs.
-
In industrial facilities, motor protection classes are critical for safety and energy efficiency.
Electric motor protection classes ensure both safety and long-term performance by matching the motor to the conditions of its operating environment.
 English
English
 Türkçe
Türkçe