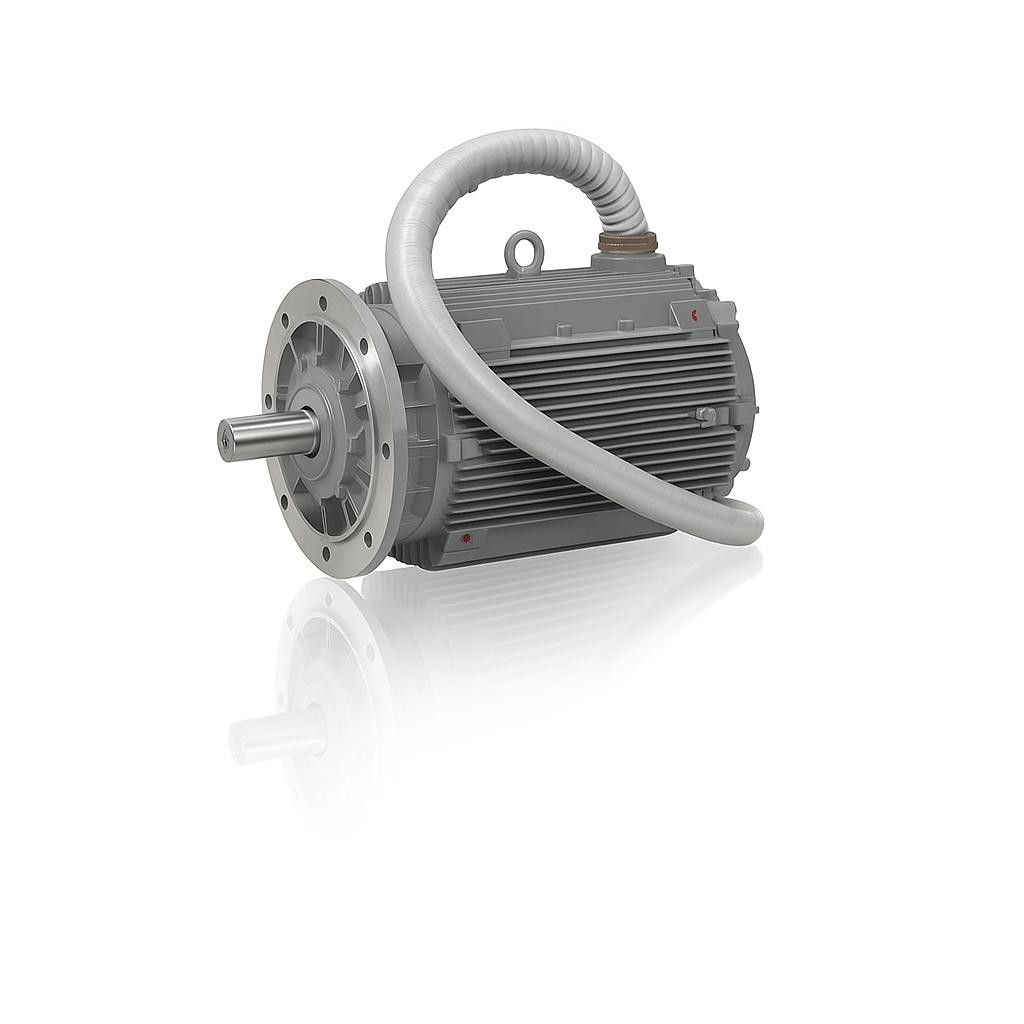
Durable Industrial Motors for Fan Systems
Contact: +90 (542) 666 11 11
Electric motors are devices that convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, and they are a fundamental part of modern life. From powering machines in factories to household appliances, from transportation systems to energy generation, electric motors are used in countless applications.
What is an Electric Motor?
An electric motor is a device that converts electrical energy into rotational motion using electromagnetic fields. This conversion allows electrical energy to perform mechanical work. Depending on the type, design, and intended use, motors come in various power and speed options.
How Electric Motors Work
Electric motors mainly consist of two components: the stator and the rotor:
-
Stator: The stationary part of the motor that generates a magnetic field when electricity flows through it.
-
Rotor: The rotating part that interacts with the stator's magnetic field to produce mechanical rotation.
Electric motors can operate with AC (Alternating Current) or DC (Direct Current) electricity. AC motors are widely used in industrial and household systems, while DC motors are preferred in low-voltage applications requiring precise control.
Types of Electric Motors
-
AC (Alternating Current) Motors
-
The most commonly used motors in industry.
-
Frequently used in fans, pumps, compressors, and conveyor systems.
-
Divided into asynchronous (induction) and synchronous motors:
-
Asynchronous motors: The rotor slightly lags behind the stator’s magnetic field, offering durability and low cost.
-
Synchronous motors: The rotor rotates at the same speed as the stator’s magnetic field, providing constant speed and high efficiency.
-
DC (Direct Current) Motors
-
Easy to control speed and torque.
-
Used in electric vehicles, robotics, and precision devices.
-
High-Efficiency Motors (IE3, IE4, IE5)
-
Reduce energy consumption and minimize overheating.
-
Preferred in modern industrial applications.
AC (Alternating Current) Motors
-
The most commonly used motors in industry.
-
Frequently used in fans, pumps, compressors, and conveyor systems.
-
Divided into asynchronous (induction) and synchronous motors:
-
Asynchronous motors: The rotor slightly lags behind the stator’s magnetic field, offering durability and low cost.
-
Synchronous motors: The rotor rotates at the same speed as the stator’s magnetic field, providing constant speed and high efficiency.
-
DC (Direct Current) Motors
-
Easy to control speed and torque.
-
Used in electric vehicles, robotics, and precision devices.
High-Efficiency Motors (IE3, IE4, IE5)
-
Reduce energy consumption and minimize overheating.
-
Preferred in modern industrial applications.
Applications of Electric Motors
-
Industry: Factory machines, pumps, fans, compressors
-
Home and Commercial: Air conditioners, refrigerators, washing machines, vacuum cleaners
-
Transportation: Electric trains, electric vehicles
-
Energy Generation: Hydroelectric, wind, and solar energy systems
Industry: Factory machines, pumps, fans, compressors
Home and Commercial: Air conditioners, refrigerators, washing machines, vacuum cleaners
Transportation: Electric trains, electric vehicles
Energy Generation: Hydroelectric, wind, and solar energy systems
Advantages of Electric Motors
-
High efficiency and long lifespan
-
Wide range of power and speed options
-
Low maintenance requirements
-
Energy-saving and environmentally friendly
High efficiency and long lifespan
Wide range of power and speed options
Low maintenance requirements
Energy-saving and environmentally friendly
DRG Motor and Electric Motors
In industrial applications, DRG Motor serves as an example of the durability and high efficiency of electric motors. It delivers reliable performance even under heavy loads and ensures long-term operation.
Conclusion
Electric motors are essential components of modern life and industry. AC and DC motors are designed to meet different needs and are indispensable for energy conversion. High-efficiency and durable motors play a critical role in energy savings and reliability. Examples like DRG Motor clearly demonstrate the technological advancement and industrial importance of electric motors.
 English
English
 Türkçe
Türkçe