Our Quick Access Phone Numbers:
+90 (542)
666 11 11
+90 (532)
345 49 86
Mail : info@drgmakina.com
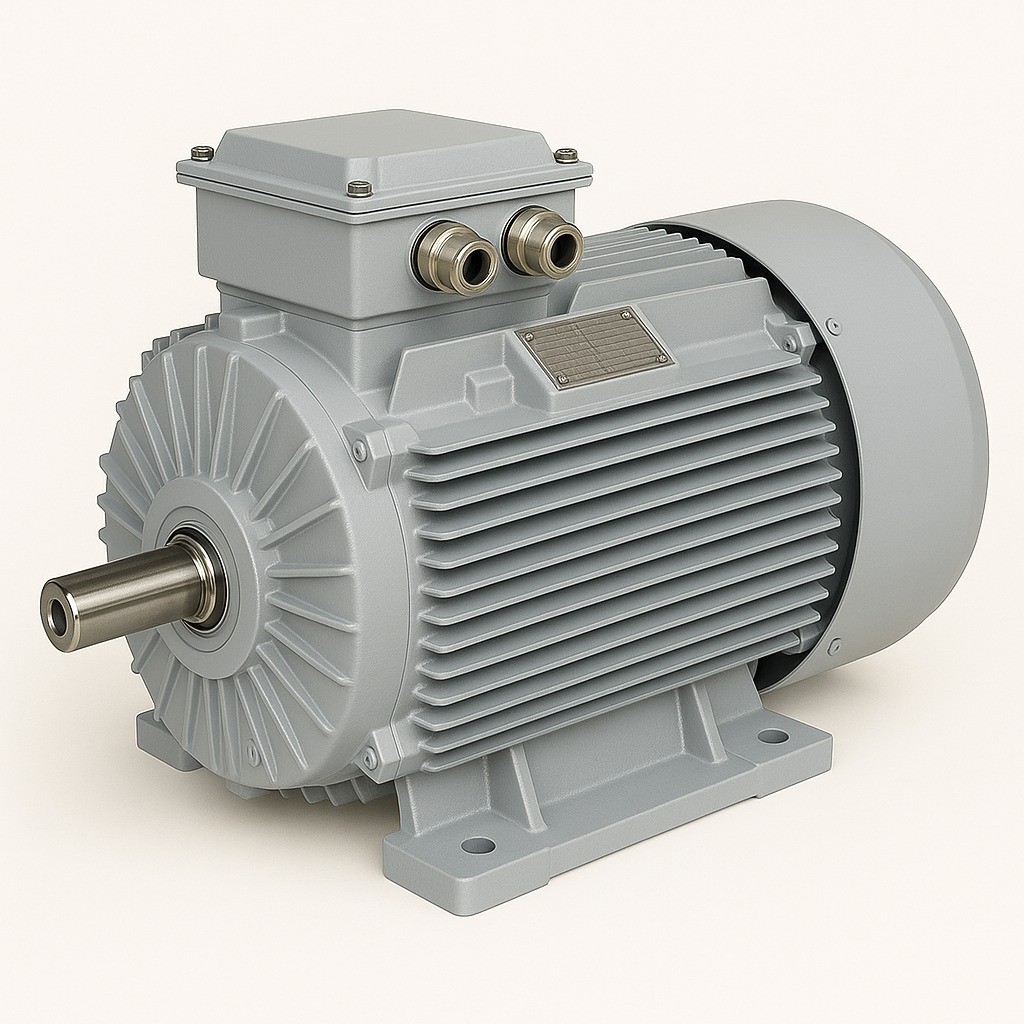
Dual-Speed Asynchronous Motors
Dual-speed asynchronous motors are AC motors capable of operating at two different speeds with a single motor. They are widely used in industrial applications where flexible speed control is required. These motors are designed to save energy, meet torque requirements, and optimize system performance.
Working Principle
Dual-speed asynchronous motors achieve two different speeds through different rotor and stator winding connections or varying pole numbers. Common methods include:
-
Pole-changing method: Changing the number of poles alters the motor’s synchronous speed, producing two operating speeds.
-
Two-winding method: Stator windings are powered separately to provide low and high-speed options.
Applications
Dual-speed asynchronous motors are particularly suitable for applications requiring variable speeds, such as:
-
Pump systems: Low speed saves energy, high speed provides high flow rate.
-
Fans: Used to provide different airflows as needed.
-
Conveyor systems: Adjusts material flow speed.
-
Processing machines: Allows variable speed control for different production stages.
Advantages
-
Provides two speeds with a single motor, eliminating the need for additional motors.
-
Saves energy, especially during low-speed operation.
-
Offers flexible usage and reduces maintenance costs.
-
Ensures reliable and durable operation in heavy industry and production applications.
Selection Criteria
When selecting a dual-speed asynchronous motor, consider:
-
Torque and speed requirements of the application
-
Motor duty cycle and load profile
-
Energy efficiency class (preferably IE3 or IE4)
-
Operating environment (temperature, dust, humidity)
-
Mechanical and mounting compatibility
Conclusion
Dual-speed asynchronous motors play a crucial role in industrial and production systems due to their flexible speed options, high durability, and energy efficiency. Proper motor selection enhances system performance, reduces operating costs, and extends motor life.
 English
English
 Türkçe
Türkçe