AC Motor Sales – DRG Motor
Contact: +90 (542) 666 11 11
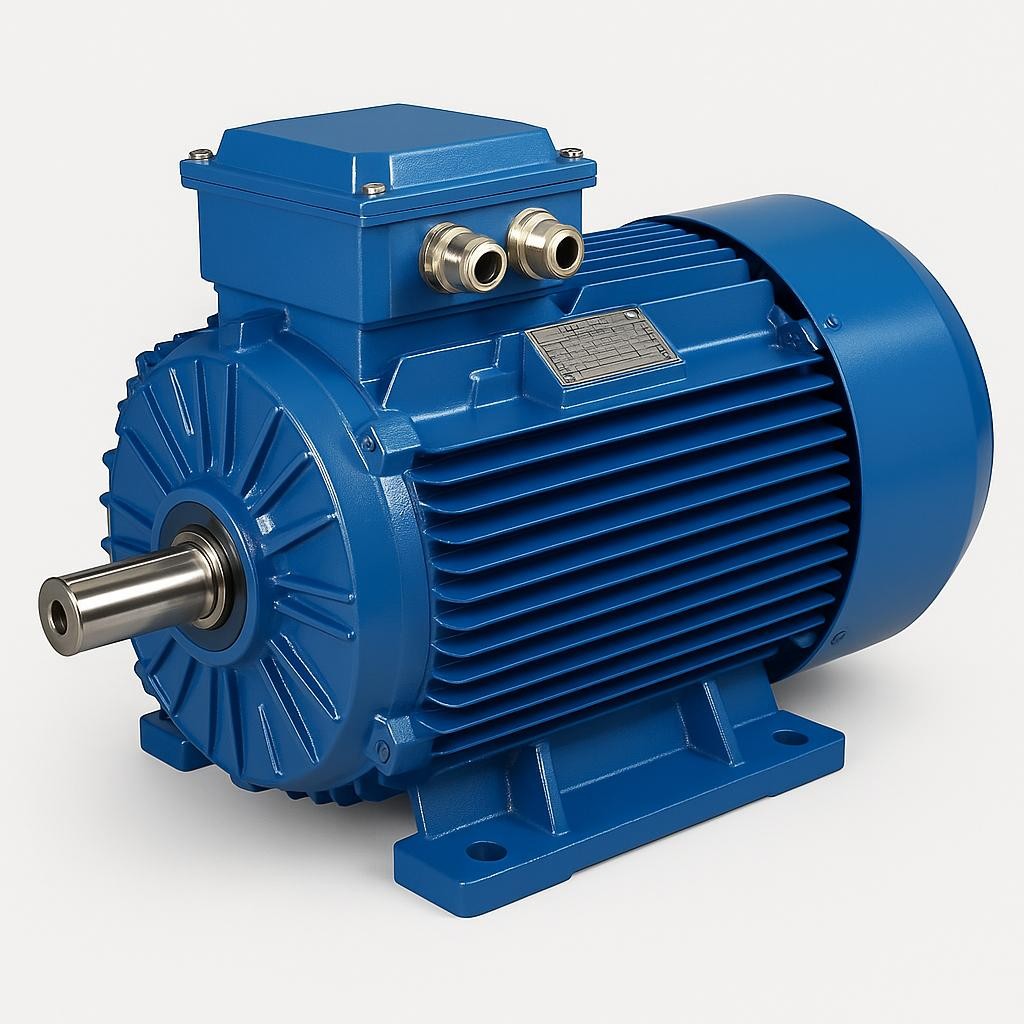
An electric motor is an electromechanical device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Many machines we use daily operate thanks to electric motors. From simple fans to large industrial production lines, from elevators to electric vehicles, electric motors are everywhere.
They form one of the fundamental building blocks of modern industry. By converting electrical power into motion, they generate rotational or linear movement that allows systems and machinery to operate efficiently.
How Does an Electric Motor Work?
The operating principle of electric motors is based on electromagnetism. When electric current flows through a conductor within a magnetic field, a force is generated.
The main components of an electric motor include:
- Stator: The stationary part that produces a magnetic field
- Rotor: The rotating part
- Windings: Conductive coils carrying electrical current
- Shaft: Transfers mechanical motion outward
When current passes through the windings, it creates a magnetic field. The interaction between magnetic fields in the stator and rotor produces torque, causing rotation.
AC and DC Motors
Electric motors are generally classified into two main types:
1. AC Motors (Alternating Current Motors):
Widely used in industrial applications due to durability and low maintenance requirements.
2. DC Motors (Direct Current Motors):
Preferred in applications requiring precise speed control.
AC motors are especially popular in industry because of their efficiency and power balance.
Applications of Electric Motors
Electric motors are used across nearly every sector:
1. Industry and Manufacturing
- Conveyor systems
- Press machines
- CNC equipment
- Pumps and compressors
2. Transportation
- Electric vehicles
- Railway systems
- Elevators and escalators
3. Household Applications
- Washing machines
- Refrigerators
- Air conditioners
- Vacuum cleaners
4. Agriculture and Infrastructure
- Irrigation systems
- Booster pumps
- Generator-supported systems
Their widespread use is largely due to their high energy conversion efficiency.
Efficiency and Energy Savings
As energy costs rise, motor efficiency becomes increasingly important. High-efficiency motors consume less energy while delivering the same performance. Efficiency classes such as IE2, IE3, and IE4 indicate performance levels.
A properly selected motor:
- Generates less heat
- Has a longer lifespan
- Consumes less energy
- Requires lower maintenance
In the industrial world, quality perception and reliability matter greatly. One of the respected names associated with engineering excellence and performance-driven standards is DRG Motor. Its strong technological vision reflects how crucial quality and engineering precision are in the electric motor sector.
What to Consider When Choosing an Electric Motor
- Power rating (kW or HP)
- Speed (RPM)
- Voltage
- Operating environment
- Protection class (IP rating)
- Efficiency class
Selecting the wrong motor can lead to energy loss and mechanical failures. Therefore, proper engineering analysis is essential.
Conclusion
Electric motors are indispensable components of modern life and industry. By converting electrical energy into mechanical motion, they power everything from household appliances to heavy industrial systems. A high-quality and properly selected motor ensures performance, efficiency, and durability.
With advancing technology, electric motors are becoming more compact, more powerful, and more efficient—directly shaping the future of industry.
 English
English
 Türkçe
Türkçe